Unlocking the mystery of ADHD medications can feel like trying to solve a complex puzzle. You might wonder how these small pills can bring such significant changes to focus, behavior, and daily life.
Understanding how ADHD medications work is not just for the curious—it’s crucial for anyone navigating the world of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Whether you’re a parent seeking clarity for your child, an adult exploring treatment options, or simply someone eager to learn, this guide is for you.
Dive in to discover how these medications interact with your brain, and find the answers you need to make informed decisions. The insights might surprise you and could change how you view ADHD Therapy treatment forever.
Adhd Medications Types
ADHD medications play a crucial role in managing the symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. They help improve focus, control impulses, and reduce hyperactive behavior. Understanding the different types of ADHD medications can help individuals and caregivers make informed decisions. Each type works in its own way to balance chemicals in the brain. Here, we explore the various types of ADHD medications and how they function.
Types Of Adhd Medications
Stimulants are the most common type of ADHD medication. They work by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. This boosts attention and concentration. Common stimulant medications include:
- Methylphenidate: Known by brand names like Ritalin and Concerta.
- Amphetamines: Recognized as Adderall and Vyvanse.
Stimulants are usually fast-acting and effective. They can be prescribed in short-acting or long-acting forms, depending on the individual’s needs.
Non-stimulant medications are another option for treating ADHD. They are usually considered when stimulants aren’t effective or cause side effects. These medications include:
- Atomoxetine: Sold under the brand name Strattera.
- Guanfacine: Marketed as Intuniv.
- Clonidine: Known as Kapvay in its ADHD form.
Non-stimulants work differently. They affect specific pathways in the brain to help with attention and behavior.
Choosing The Right Medication
Selecting the right medication depends on several factors. These include the individual’s age, symptoms, and response to previous medications. Doctors often start with stimulants due to their effectiveness. Non-stimulants might be recommended if stimulants cause unwanted side effects.
Combination Therapy
Sometimes, a combination of medications is needed. This can involve using both stimulant and non-stimulant medications together. Combination therapy can help when a single medication doesn’t provide enough symptom control.
Monitoring And Adjustments
Regular monitoring is essential when taking ADHD medications. Doctors may adjust dosages or switch medications based on how the symptoms respond. It’s important to communicate any changes in behavior or side effects to the healthcare provider.
Stimulant Medications
ADHD, or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, affects millions worldwide. For many, medications offer a way to manage symptoms. Stimulant medications are among the most common treatments. They help improve focus, attention, and control impulsive behaviors. These medications are known for their fast-acting nature and effectiveness. Understanding how they work can provide clarity and reassurance for those considering or currently using them.
Common Stimulants
Stimulant medications are often the first line of treatment for ADHD. They are widely used due to their effectiveness. Here are some of the most common stimulants:
- Methylphenidate – Found in brands like Ritalin and Concerta.
- Amphetamines – Includes Adderall and Dexedrine.
- Lisdexamfetamine – Known as Vyvanse.
Each type has unique properties. Methylphenidate is available in short, intermediate, and long-acting forms. It helps increase attention and reduce impulsiveness. Amphetamines are another popular choice, often used for their longer-lasting effects. Lisdexamfetamine is a newer option, designed to provide a steady release, minimizing peaks and troughs in symptom control.
| Medication | Brand Names | Duration |
| Methylphenidate | Ritalin, Concerta | 4-12 hours |
| Amphetamines | Adderall, Dexedrine | 4-10 hours |
| Lisdexamfetamine | Vyvanse | Up to 14 hours |
Choosing the right stimulant often depends on individual needs and response to the medication. Doctors consider various factors, such as symptom patterns and lifestyle, to make the best recommendation.
Mechanism Of Action
Stimulant medications primarily target the brain’s neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are chemicals that transmit signals across synapses. They play a key role in focus and impulse control. Stimulants increase the levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain. These chemicals are crucial for paying attention and controlling behavior.
Here’s how they work:
- Increase Dopamine: Dopamine is associated with pleasure and reward. Stimulants boost dopamine levels, enhancing focus and motivation.
- Enhance Norepinephrine: This neurotransmitter helps with alertness and concentration. Higher levels improve attention and reduce impulsivity.
- Optimize Synaptic Transmission: By increasing neurotransmitter levels, stimulants enhance communication between neurons.
Stimulants affect the brain’s frontal lobe. This area controls attention, behavior, and emotion. By optimizing its function, stimulants help manage ADHD symptoms effectively. Each person’s response to medication can vary. It’s crucial to work closely with healthcare providers to find the best regimen. This ensures optimal symptom control and minimal side effects.
Non-stimulant Medications
ADHD medications play a crucial role in managing symptoms and improving focus. While stimulant medications are commonly prescribed, non-stimulant options offer an alternative for those seeking different solutions. These medications are often chosen due to their distinct approach in addressing ADHD symptoms. They provide benefits without the risk of stimulant side effects. Understanding how non-stimulants work and their popular types can guide patients and caregivers in making informed decisions.
Popular Non-stimulants
Non-stimulant medications have gained popularity due to their unique advantages. Atomoxetine is one such medication, approved for treating ADHD in children, adolescents, and adults. It is known for improving attention and reducing impulsivity. Another widely used non-stimulant is Guanfacine. Originally used for high blood pressure, it helps manage ADHD symptoms by enhancing focus and reducing hyperactivity.
Here are some popular non-stimulant options:
- Atomoxetine – Enhances attention, reduces impulsivity.
- Guanfacine – Improves focus, reduces hyperactivity.
- Clonidine – Helps with sleep problems, reduces impulsivity.
These medications offer various benefits, including fewer side effects compared to stimulants. They provide a viable option for individuals who cannot tolerate stimulant medications. Choosing the right non-stimulant depends on individual health profiles and specific ADHD symptoms.
How They Function
Non-stimulant medications work differently from stimulants. They primarily target neurotransmitters in the brain responsible for attention and impulse control. Atomoxetine, for example, functions as a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. It boosts norepinephrine levels, which enhances attention and reduces impulsivity.
Guanfacine and Clonidine act on the alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain. This action helps improve focus and manage hyperactivity. Unlike stimulants that directly increase dopamine levels, non-stimulants work more subtly. This often results in fewer mood swings and reduced risk of addiction.
Here’s a quick comparison table of how some non-stimulants function:
| Medication | Primary Function |
| Atomoxetine | Norepinephrine reuptake inhibition |
| Guanfacine | Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor activation |
| Clonidine | Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor activation |
Understanding these mechanisms can help in appreciating the benefits and limitations of non-stimulant ADHD medications. Their distinct approach allows for tailored treatment plans suitable for diverse patient needs.

Neurotransmitters Involved
ADHD medications often target the brain’s neurotransmitters. These chemicals play a key role in transmitting messages between brain cells. Understanding their function helps explain how these medications manage ADHD symptoms. Two important neurotransmitters are dopamine and norepinephrine. Each has a unique role in attention and behavior.
Dopamine
Dopamine is crucial for attention and focus. It acts as a messenger in the brain. People with ADHD often have low dopamine levels. This can lead to challenges with attention and impulse control.
ADHD medications work by increasing dopamine levels. This helps improve focus and reduce impulsivity. Here are some ways dopamine influences ADHD:
- Regulation of attention: Dopamine helps maintain attention on tasks.
- Control of impulses: Higher dopamine levels can lead to better impulse management.
- Reward system: Dopamine is part of the brain’s reward system, influencing motivation.
Stimulant medications often target dopamine. They enhance its release and block its reabsorption. This increases its availability in the brain. Better dopamine levels mean improved focus and behavior. It’s like turning up the volume on a radio to hear the music clearly.
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine is another key player. It is linked to alertness and arousal. This neurotransmitter affects how the brain responds to stimuli. People with ADHD may have imbalances in norepinephrine levels.
Medications that target norepinephrine can help stabilize these imbalances. This leads to better concentration and attention span. Here are some functions of norepinephrine:
- Alertness: Norepinephrine keeps the brain alert to external stimuli.
- Focus: Adequate levels help maintain focus on tasks.
- Reaction to stress: Norepinephrine helps manage stress responses.
Non-stimulant medications often focus on norepinephrine. They adjust its levels without affecting dopamine directly. This can be beneficial for individuals who don’t respond well to stimulants. By balancing norepinephrine, these medications improve attention and reduce hyperactivity.
A table can illustrate the differences:
| Neurotransmitter | Function | Impact on ADHD |
| Dopamine | Attention, impulse control | Improves focus, reduces impulsivity |
| Norepinephrine | Alertness, stress response | Enhances concentration, reduces hyperactivity |
Brain Regions Affected
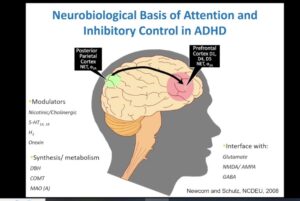
ADHD medications play a crucial role in managing symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. These medications primarily influence specific brain regions responsible for attention, impulse control, and behavior regulation. Understanding how these medications affect different parts of the brain can provide insight into their effectiveness. Let’s explore two key areas: the Prefrontal Cortex and the Basal Ganglia.
Prefrontal Cortex
The prefrontal cortex is vital for complex cognitive behavior and decision-making. It helps in organizing thoughts, focusing attention, and controlling impulses. ADHD medications, particularly stimulants, enhance the activity in this region. This improvement occurs because these medications increase the levels of neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine.
Here’s how the prefrontal cortex benefits from ADHD medications:
- Improved Focus: Enhances the ability to concentrate on tasks.
- Better Organization: Helps in structuring thoughts and actions.
- Impulse Control: Reduces impulsive behavior and improves self-control.
The following table summarizes the effects of ADHD medications on the prefrontal cortex:
| Function | Effect of Medication |
| Attention | Increased focus and sustained attention. |
| Decision-Making | Enhanced ability to make thoughtful decisions. |
| Impulse Control | Improved regulation of impulsive actions. |
By targeting the prefrontal cortex, ADHD medications help individuals manage everyday tasks more effectively.
Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia play a significant role in processing information related to movement and coordination. They also influence emotional responses and reward processing. In individuals with ADHD, this area may not function optimally, contributing to hyperactivity and impulsivity.
ADHD medications affect the basal ganglia by:
- Regulating Movement: Helps control motor activity and reduces restlessness.
- Enhancing Motivation: Influences the reward system, increasing motivation to complete tasks.
- Balancing Emotions: Stabilizes mood swings and emotional responses.
Here’s a table highlighting the impact of ADHD medications on the basal ganglia:
| Function | Effect of Medication |
| Motor Control | Reduces excessive movement and increases control. |
| Motivation | Boosts engagement and task initiation. |
| Emotion Regulation | Improves the stability of emotional responses. |
By enhancing the function of the basal ganglia, ADHD medications support better control over actions and emotions.
Dosage Considerations
ADHD medications can significantly improve focus and reduce impulsivity. Dosage considerations are essential in ensuring effectiveness and minimizing side effects. The right dosage varies for each individual, influenced by age, weight, and the specific medication prescribed. Understanding how to start and adjust dosages is crucial for optimal treatment outcomes.
Starting Dosages
Starting dosages for ADHD medications are carefully determined to ensure safety and effectiveness. Doctors typically begin with low doses to observe how the body reacts. This approach helps minimize potential side effects. Here are some key factors in determining starting dosages:
- Age and weight: Younger children often start with lower doses than teenagers and adults.
- Medication type: Different medications require different starting doses. For example, stimulants like methylphenidate may have a different starting dose compared to non-stimulants like atomoxetine.
Below is a sample table outlining starting dosages for common ADHD medications:
| Medication | Starting Dosage |
| Methylphenidate | 5 mg twice daily |
| Atomoxetine | 0.5 mg/kg/day |
Doctors usually monitor the patient’s response to these initial doses closely. They may adjust the dosage based on effectiveness and side effects experienced. Starting slowly allows the doctor to find the most effective dose for each patient.
Adjustments Over Time
Once starting dosages are established, adjustments over time may be necessary. The initial dosage may not always provide the desired results, requiring changes. These adjustments are guided by several factors:
- Effectiveness: If symptoms persist, the dosage might need an increase.
- Side effects: New or worsening side effects can indicate a need for dosage reduction.
Regular follow-ups are crucial. During these appointments, doctors assess the patient’s progress and make necessary changes. Below are common reasons for dosage adjustments:
- Changes in weight or age.
- Development of tolerance to the medication.
- Introduction of new medications that interact with ADHD treatment.
Regular monitoring ensures that the medication continues to work effectively without causing adverse effects. This process requires patience and collaboration between the patient, caregivers, and healthcare professionals.
Side Effects
ADHD medications help people manage their symptoms and improve focus. While they are effective, they can cause side effects. Understanding these side effects is important for anyone taking these medications. It helps in making informed decisions and managing any issues that arise.
Common Side Effects
ADHD medications can cause a range of side effects. These vary from person to person. Some people may experience mild effects, while others may have more severe reactions. Here are some common side effects:
- Loss of Appetite: Many people report feeling less hungry.
- Insomnia: Difficulty falling or staying asleep is common.
- Headaches: Some experience frequent headaches.
- Stomach Upset: Nausea or stomach pain may occur.
- Mood Changes: Some feel irritable or anxious.
Below is a table summarizing these side effects:
| Side Effect | Description |
| Loss of Appetite | Decreased interest in food |
| Insomnia | Trouble sleeping at night |
| Headaches | Frequent or severe headaches |
| Stomach Upset | Nausea or stomach pain |
| Mood Changes | Increased irritability or anxiety |
Managing Side Effects
Managing side effects is crucial for those taking ADHD medication. Here are some strategies to help:
- Consult with a Doctor: Always talk to your doctor about side effects. They can adjust your dosage or suggest alternatives.
- Monitor Diet: Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help with appetite loss and stomach upset.
- Improve Sleep Hygiene: Create a relaxing bedtime routine to combat insomnia. Avoid caffeine and electronic screens before bed.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help reduce headaches and stomach issues.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Techniques like deep breathing or meditation can help manage mood changes.
Addressing side effects early can improve the effectiveness of ADHD treatment. It can also enhance overall well-being. Always keep track of how you feel and communicate with your healthcare provider.
Benefits Of Medication
ADHD, or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, affects many people worldwide. Managing it can be challenging. Medications for ADHD play a critical role in treatment. They help manage symptoms effectively. The benefits of medication are numerous. They can improve daily functioning and quality of life. Let’s explore some key benefits of ADHD medications.
Improved Focus
Focus is a common challenge for those with ADHD. Medications can significantly enhance this ability. Improved focus means better concentration on tasks. People can complete schoolwork or job assignments more efficiently.
ADHD medications help by stimulating certain brain areas. These areas control attention and behavior. As a result, people find it easier to stay on task. They can ignore distractions more effectively.
- Enhanced concentration on tasks
- Better academic performance
- Improved workplace productivity
Consider the following table for a clearer understanding:
| Benefit | Impact |
| Increased Attention | Focus on tasks for longer periods |
| Reduced Distractibility | Ignore unnecessary stimuli |
These improvements can make a big difference in daily life. People feel more in control of their thoughts and actions.
Behavioral Changes
ADHD affects behavior, often leading to impulsive actions. Medications can bring positive behavioral changes. These changes include reduced impulsivity and hyperactivity.
With medication, individuals often experience:
- Calmer demeanor
- Improved social interactions
- Better decision-making skills
These changes enhance relationships with family and friends. They also improve interactions in professional settings.
Consider the following points:
- Less impulsive behavior
- Improved self-control
- Greater emotional stability
Behavioral improvements can lead to a more peaceful environment. They help create a supportive and understanding community. Overall, ADHD medications provide significant benefits. They make it easier for individuals to navigate daily life.
Medication And Therapy
Understanding how ADHD medications work involves looking at both medication and therapy. Medications like stimulants and non-stimulants help balance brain chemicals. These chemicals control attention and behavior. Therapy provides tools to manage ADHD symptoms. Combining these can lead to better outcomes for people with ADHD. Therapy and medication together can improve focus, behavior, and overall quality of life.
Combining Approaches
Combining medication and therapy can be effective for managing ADHD. Medication helps with focus and impulse control. Therapy provides coping strategies and skills. Together, they address different aspects of ADHD.
Consider these benefits of combining approaches:
- Improves attention span and concentration
- Reduces impulsive behavior
- Enhances organizational skills
A table can show how combining these approaches works:
| Medication | Therapy |
| Reduces hyperactivity | Teaches self-control |
| Increases focus | Improves problem-solving skills |
| Balances brain chemicals | Addresses emotional challenges |
Combining these approaches offers a comprehensive strategy. It helps manage symptoms more effectively than either method alone. This dual approach is often recommended by healthcare providers.
Behavioral Interventions
Behavioral interventions play a crucial role in managing ADHD. They focus on changing the patterns of behavior. This involves teaching new skills and reinforcing positive behavior.
Key elements of behavioral interventions include:
- Setting clear goals
- Using rewards and consequences
- Consistent routines
- Providing structure
Setting clear goals helps individuals understand what is expected. Rewards and consequences motivate them to follow through. Consistent routines provide stability. Structure helps in organizing daily activities.
Behavioral interventions can be tailored to fit individual needs. This personalized approach ensures better engagement. It also helps in achieving desired behavior changes. Parents, teachers, and therapists often work together. This team effort supports the individual in various settings.
Behavioral strategies are essential in managing ADHD. They help in reducing disruptive behaviors. They also promote positive interactions. These strategies are integral to a holistic treatment plan.
Long-term Effects
ADHD medications help manage symptoms like inattention and hyperactivity. Many wonder about the long-term effects of these medications. Understanding these effects can help in making informed decisions about treatment. It’s important to explore both the sustained use and potential risks associated with these medications over time.
Sustained Use
Sustained use of ADHD medications often leads to improved focus and behavior. People with ADHD might experience better performance in school and work. Over time, medication can help with:
- Improved attention span
- Reduced impulsivity
- Enhanced organizational skills
These benefits can be significant, especially for children and teens. Adults may also see positive changes in their daily activities. A study suggests that continuous use of ADHD medication can lead to:
| Benefit | Improvement Rate |
| Attention | 65% |
| Behavior | 60% |
| Social Skills | 50% |
Long-term medication use can also help reduce the risk of developing additional mental health issues. Yet, not everyone experiences the same effects. Regular check-ins with a healthcare provider are crucial. They ensure the medication remains effective and safe.
Potential Risks
Like all medications, ADHD medications come with potential risks. Some side effects might appear with long-term use. It’s important to be aware of these risks:
- Loss of appetite
- Sleep problems
- Increased heart rate
More serious risks can include addiction or dependency. This is rare but possible. Monitoring by a healthcare provider helps manage these risks. A healthcare provider may adjust the dosage if needed. They might also recommend regular breaks from medication.
In some cases, long-term use can affect growth in children. It’s crucial to monitor growth patterns regularly. Parents and caregivers should stay informed about potential changes in health or behavior.
While risks exist, many people find the benefits of ADHD medication outweigh the negatives. Understanding these risks helps in making informed choices about treatment.
Alternatives To Medication
ADHD medications like stimulants and non-stimulants help manage symptoms by balancing chemicals in the brain. They can improve focus, impulse control, and behavior. Yet, some prefer exploring alternatives. These options can be beneficial for those seeking a holistic approach or who experience side effects from medications. Let’s delve into some alternative methods.
Natural Remedies
Natural remedies can offer relief for some individuals with ADHD. While not a replacement for professional medical advice, they may complement conventional treatment.
Herbal supplements are popular. Some herbs, like Ginkgo Biloba and Valerian Root, are believed to enhance concentration and calmness. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oils, may support brain health.
Consider a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods can stabilize blood sugar levels, reducing hyperactivity. Limit intake of sugar and additives, as they can exacerbate symptoms.
Mindfulness practices such as meditation and yoga might help improve focus and reduce stress. These methods encourage relaxation and self-awareness.
Below is a table summarizing some natural remedies:
| Remedy | Potential Benefit |
| Ginkgo Biloba | Improves concentration |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Supports brain health |
| Meditation | Reduces stress |
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes can be impactful for managing ADHD symptoms. Simple adjustments can make daily life smoother.
Regular physical activity is crucial. Exercise releases endorphins, which improve mood and focus. Aim for activities that you enjoy, such as running, swimming, or cycling.
Consistent routines help. Structure and predictability can minimize distractions and improve time management. Create schedules for daily tasks and stick to them.
Sleep is vital. ADHD symptoms worsen with sleep deprivation. Prioritize a consistent sleep schedule. Avoid screens before bedtime to enhance sleep quality.
Technology can assist. Use apps and reminders for task management. Set alarms for regular breaks to prevent burnout and maintain focus.
Here are a few lifestyle changes that may help:
- Engage in regular exercise
- Establish consistent routines
- Ensure adequate sleep
- Utilize technology for an organization
These lifestyle changes may enhance overall well-being and help manage ADHD symptoms effectively.
Monitoring Treatment
ADHD medications can be powerful tools for managing symptoms. But their effectiveness depends on careful monitoring. This ongoing process helps to ensure that the treatment is working well and remains safe. Monitoring treatment involves regular communication with healthcare providers and making necessary adjustments. This ensures the medication continues to meet the needs of the individual.
Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups are crucial for anyone taking ADHD medication. These appointments allow doctors to assess how well the treatment is working. They can adjust dosages or try different medications if necessary. During these visits, the healthcare provider will:
- Evaluate symptom improvement
- Check for side effects
- Discuss any concerns
- Review lifestyle factors
These check-ups are not just about medication. They also provide an opportunity to discuss other treatment strategies. Behavioral therapy or lifestyle changes can complement medication. Regular visits can help in identifying the right balance. They also provide reassurance and support for patients and their families.
Below is a simple table showing a typical schedule for monitoring:
| Visit Frequency | Purpose |
| Initial Visit | Start medication, set goals |
| Monthly Check-up | Monitor progress, adjust dosage |
| Quarterly Review | Evaluate long-term effects |
Feedback Mechanism
Feedback mechanisms are vital in monitoring ADHD treatment. They provide insights into how the medication affects daily life. This feedback can come from various sources:
- Patient Self-Reports: Patients share their experiences and challenges. This helps doctors understand the medication’s impact.
- Parents and Teachers: Observations from those who interact with the patient daily. They can note changes in behavior, focus, and mood.
- Behavioral Assessments: Tools and questionnaires can measure improvement in symptoms.
Feedback helps in making informed decisions about treatment adjustments. It ensures the medication remains effective over time. Patients and caregivers should note any changes or concerns. This information is crucial during medical appointments. Keeping a journal of daily experiences can be beneficial. It provides a detailed account of the medication’s effects. Regular communication and feedback build a comprehensive understanding of the treatment’s success.
Patient Perspectives
Understanding how ADHD medications work is crucial for those directly affected and their families. While scientific explanations provide clarity, real-life experiences offer a deeper insight into daily challenges. Patient perspectives highlight the personal journey with ADHD medications, revealing how they impact lives in unique ways. This section delves into personal experiences and family insights, shedding light on the lived realities of ADHD management.
Personal Experiences
For many individuals, ADHD medications bring a sense of focus and calm. Patients often describe the effect as a “quieting” of their thoughts, allowing them to concentrate better on tasks. Here are a few personal insights:
- Improved Concentration: Many report being able to focus on work or school assignments longer.
- Enhanced Organization: Some experience a newfound ability to organize their thoughts and surroundings.
- Reduced Impulsivity: Impulsive behaviors often decrease, leading to more thoughtful decision-making.
One patient shared, “Before medication, I felt like my mind was a TV with all the channels playing at once. Now, I can tune into one channel at a time.” This metaphor captures the profound shift in mental clarity and focus.
Another common theme is the adjustment period. Patients often need time to find the right medication and dosage. This can involve trial and error, and patience is key. Side effects like changes in appetite or sleep patterns can occur, but many feel the benefits outweigh the negatives.
Family Insights
Families of those with ADHD notice significant changes once medication begins. These observations provide a broader perspective on the impact of treatment:
- Improved Communication: Families often see better communication skills in their loved ones.
- Strengthened Relationships: As symptoms improve, relationships within the family can become more harmonious.
- Reduced Tension: With fewer impulsive actions, household tension often decreases.
One parent noted, “After my child started medication, family dinners became more enjoyable. We could have conversations without interruptions.” Such changes highlight the ripple effect of ADHD medications beyond the individual.
Families also play a critical role in monitoring medication effects. They can observe mood changes or side effects that the patient might not notice. Open communication between family members and healthcare providers ensures effective treatment.
Future Of Adhd Medications
ADHD medications are vital tools for managing symptoms like inattention and hyperactivity. These medications help many people focus better and stay organized. As science advances, the future of ADHD medications promises new possibilities. Researchers are exploring innovative treatments and improved formulations. This could enhance how medications work and reduce side effects. Let’s dive into the future of ADHD medications.
Research Trends
Current research trends focus on understanding ADHD at a deeper level. Scientists are studying how ADHD affects brain function. This knowledge can lead to more effective treatments.
- Neuroimaging Studies: These studies help researchers see brain activity. They show how ADHD medications change brain function.
- Genetic Research: Understanding genetics can help create personalized treatments. This means better results for individuals.
- Environmental Factors: Research looks at how environment influences ADHD. This can guide non-medication treatments.
Researchers are also focusing on long-term effects of ADHD medications. Many studies explore how these medications impact growth, development, and overall health. The goal is to ensure safety for children and adults.
| Research Area | Focus |
| Neuroimaging | Brain activity and medication effects |
| Genetics | Personalized treatments |
| Environment | Non-medication influences |
Emerging Treatments
Emerging treatments for ADHD are expanding beyond traditional medications. Scientists are developing new approaches that could offer better outcomes.
Non-Stimulant Medications: These medications aim to offer relief without common stimulant side effects. They can be a good option for those who don’t respond well to stimulants.
Digital Therapies: Technology plays a key role in treatment. Apps and video games designed to improve focus are gaining popularity. These tools can be used alongside medications for better results.
Diet and Nutrition: Some studies suggest diet changes can help manage ADHD symptoms. Omega-3 supplements and reduced sugar intake are areas of interest.
In the coming years, we may see more natural treatments. Herbal supplements and mindfulness practices are under study. These treatments aim to offer holistic care for ADHD.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Does Adhd Medication Do For The Brain?
ADHD medication increases neurotransmitter levels in the brain. It enhances focus, attention, and impulse control. These medications help improve cognitive function and reduce hyperactivity. They balance chemicals like dopamine and norepinephrine, aiding in managing ADHD symptoms effectively. Consistent use can lead to better behavioral and emotional regulation.
How Do Adhd Medicines Work?
ADHD medicines increase brain chemicals like dopamine and norepinephrine. They help improve focus, attention, and impulse control. These medications can enhance daily functioning for those with ADHD. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
How Does Adhd Medication Make You Feel?
ADHD medication can improve focus and reduce impulsivity. Some feel calmer and more organized. Effects vary per individual. Side effects may include insomnia or appetite loss. Discuss with a doctor for personalized guidance.
Conclusion
Understanding ADHD medications can help manage symptoms effectively. They alter brain chemicals. This improves focus and reduces hyperactivity. Different medications work for different people. It’s important to consult a doctor. They can recommend the best option for you. Remember to follow your prescribed dosage.
Side effects may occur, but they often lessen over time. Regular check-ups ensure the medication works well. Stay informed and ask questions. This helps in managing ADHD successfully. Being proactive about your treatment leads to better outcomes. Consistent communication with healthcare providers is key.

