Are you or someone you care about struggling with depression? You’re not alone, and there is hope.
Imagine a life where your thoughts don’t weigh you down and you can enjoy the little moments that make life beautiful. That’s where Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) comes in. It’s not just another therapy buzzword; it’s a powerful, evidence-based approach that has helped countless people find relief from depression.
By reading further, you’ll discover how CBT can transform your thought patterns and improve your mood. Stay with us to learn how this therapy might be the key to unlocking a brighter, more fulfilling life for you or your loved one.
What Is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy?
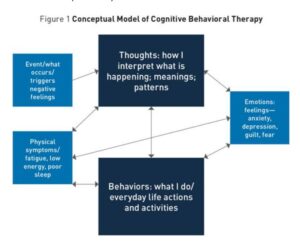
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, often abbreviated as CBT, is a well-known method for treating depression. It’s a powerful tool that helps individuals challenge and change unhelpful thoughts and behaviors. Depression can feel like a heavy cloud, but CBT aims to break that cycle and introduce positive thinking patterns. Let’s explore this effective therapy further.
CBT is a type of psychotherapy. It focuses on altering negative thought patterns. The core idea is that thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected. By changing negative thoughts, you can change how you feel and act.
CBT is structured and goal-oriented. Sessions are typically focused on specific problems. Patients work with therapists to set achievable goals. They learn to identify and challenge distorted thoughts.
How Does CBT Work?
The process of CBT involves several steps. First, you identify negative thoughts. These are often automatic and seem true, but they aren’t. Next, you challenge these thoughts. Ask yourself: Is this thought based on facts? Finally, you replace them with balanced thoughts.
Key Components Of CBT
| Component | Description |
| Cognitive Restructuring | Changing negative thoughts to positive ones. |
| Behavioral Activation | Engaging in activities that improve mood. |
| Skill Development | Learning new skills to handle stress. |
- Helps in recognizing and changing negative thinking patterns.
- Provides tools to manage stress and anxiety.
- Improves problem-solving skills.
- Encourages a more positive outlook on life.
Cbt Techniques
Various techniques are used in CBT. Cognitive restructuring helps reframe negative thoughts. Mindfulness teaches staying present. Exposure therapy addresses fears by gradual exposure. All these techniques aim to empower individuals. They learn to take control of their thoughts and feelings.
Core Principles Of CBT
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a common and effective treatment for depression. This therapy helps people understand and change their thought patterns. Changing these patterns can improve feelings and behaviors. CBT is based on several core principles. These principles guide the therapy process and help people manage their depression.
Understanding Cognitive Distortions
Cognitive distortions are inaccurate thoughts that can lead to negative feelings. People with depression often have these distortions. Examples include thinking in absolutes, like “always” or “never,” and overgeneralizing situations. CBT helps people identify and challenge these distortions. By doing this, they learn to think more realistically.
Behavioral Activation
Depression often leads to inactivity. People may stop doing things they once enjoyed. Behavioral activation encourages people to engage in positive activities. This can improve mood and reduce depressive symptoms. Simple tasks like walking or meeting a friend can make a difference.
Problem-solving Skills
Depression can make problems feel overwhelming. CBT teaches effective problem-solving skills. People learn to break down problems into smaller steps. They also learn to develop practical solutions. This approach makes challenges feel more manageable.
Identifying Core Beliefs
Core beliefs are deep-seated views about oneself, others, and the world. These beliefs can contribute to depression. CBT helps people uncover these beliefs. Once identified, therapists and clients work to modify any negative beliefs. This change can lead to improved self-esteem and outlook.
Goal Setting
Setting achievable goals is a key part of CBT. Goals provide direction and motivation. They help people focus on positive change. Goals can be short-term or long-term. They are tailored to each individual’s needs and situation. Achieving these goals can boost confidence and reduce depression.
| Core Principle | Purpose |
| Cognitive Distortions | Identifies and challenges negative thoughts |
| Behavioral Activation | Encourages engagement in enjoyable activities |
| Problem-Solving | Develops practical solutions to challenges |
| Core Beliefs | Modifies negative beliefs about self and others |
| Goal Setting | Focuses on achievable personal goals |
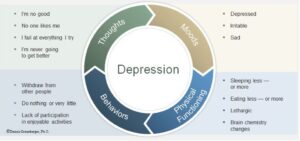
Symptoms Of Depression
Depression is a common mental health issue affecting millions globally. It can disrupt daily life, making even simple tasks seem overwhelming. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is an effective treatment for depression. It helps people change negative thought patterns and behaviors. Understanding the symptoms of depression is crucial for seeking help. Recognizing these signs can be the first step toward recovery.
Emotional Symptoms
Depression often causes persistent feelings of sadness or hopelessness. People may feel empty or numb. These emotions can last for weeks or months. Loss of interest in activities once enjoyed is common. Individuals may also feel guilt or worthlessness without reason.
Physical Symptoms
Depression can manifest physically. Fatigue is a frequent complaint. Even with adequate sleep, people may feel tired all the time. Changes in appetite can occur, leading to weight loss or gain. Sleep disturbances such as insomnia or excessive sleeping, are also symptoms.
Cognitive Symptoms
Cognitive abilities can be affected by depression. Difficulty concentrating or making decisions is common. Memory problems might arise, making it hard to remember tasks or conversations. Indecisiveness can become a frequent challenge.
Behavioral Symptoms
Depression can alter behavior. People might withdraw from social activities. Avoiding friends and family is typical, as is neglecting responsibilities. Decreased productivity at work or school can also be a sign.
| Symptom Type | Examples |
| Emotional | Sadness, hopelessness, loss of interest |
| Physical | Fatigue, changes in appetite, sleep disturbances |
| Cognitive | Difficulty concentrating, memory problems, indecisiveness |
| Behavioral | Withdrawal from activities, neglecting responsibilities, decreased productivity |
How CBT Addresses Depression
Depression can feel like a heavy cloud that refuses to lift. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) offers a structured way to address depression’s underlying causes. This therapy helps individuals understand and change their thought patterns and behaviors. Through CBT, patients learn to tackle negative thoughts and replace them with healthier ones. It empowers individuals to take control of their mental health and improve their overall well-being.
Understanding Negative Thought Patterns
CBT helps identify and challenge negative thought patterns. These thoughts often worsen depression symptoms. Therapists encourage patients to recognize automatic thoughts that are unrealistic or harmful. By questioning these thoughts, patients can see them in a new light.
- Recognizing negative thoughts
- Understanding the impact on mood
- Developing healthier perspectives
Behavioral Activation
Depression often leads to a lack of motivation. CBT uses behavioral activation to combat this. It involves engaging in activities that bring pleasure or a sense of achievement. These actions can slowly improve mood and increase motivation.
| Activity | Benefit |
| Exercise | Boosts energy levels |
| Socializing | Reduces feelings of isolation |
| Creative hobbies | Enhances mood |
Developing Coping Strategies
CBT teaches coping strategies to manage stress and emotional challenges. Patients learn techniques to handle challenging situations without feeling overwhelmed. These strategies include relaxation methods and problem-solving skills.
- Relaxation techniques
- Effective communication skills
- Problem-solving methods
Setting Realistic Goals
Setting realistic goals is crucial in overcoming depression. CBT emphasizes creating achievable targets. These goals encourage small steps toward improvement, offering a sense of accomplishment and hope.
CBT provides a practical approach to address depression. By focusing on thoughts and behaviors, individuals can regain control and improve their mental health.
CBT Techniques For Depression
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a proven method for treating depression. It focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. CBT techniques help individuals manage their depression effectively. These techniques empower individuals to recognize unhelpful thoughts and develop healthier ways of thinking. By focusing on the present and future, CBT encourages a proactive approach to mental health. Let’s explore some effective CBT techniques for depression.
Cognitive Restructuring
Cognitive restructuring is a key CBT technique. It involves identifying and challenging negative thought patterns. Many people with depression experience automatic negative thoughts. These thoughts can be distorted and lead to a negative self-view.
Steps in cognitive restructuring:
- Identify negative thoughts
- Challenge these thoughts
- Replace with positive, realistic thoughts
For example, someone might think, “I am a failure.” Cognitive restructuring helps them see evidence against this thought. They might list achievements or positive feedback. This technique helps in reducing the power of negative thoughts.
| Negative Thought | Challenge | Positive Thought |
| I can’t do anything right. | Recall a recent success. | I can succeed with effort. |
Behavioral Activation
Behavioral activation is another effective CBT technique. It focuses on increasing engagement in meaningful activities. People with depression often withdraw from activities they once enjoyed. This withdrawal can worsen depression.
Key steps in behavioral activation:
- Identify enjoyable activities
- Schedule these activities
- Gradually increase participation
Engagement in positive activities can improve mood. It creates a sense of achievement and reduces depressive symptoms. Simple actions like taking a walk or calling a friend can make a difference.
Behavioral activation encourages people to break the cycle of inactivity. It promotes a more active and fulfilling life.
Exposure Therapy
Exposure therapy is useful for those with depression and anxiety. It involves facing fears in a controlled way. Many people with depression avoid situations that trigger anxiety. This avoidance can reinforce fear and negative feelings.
Steps in exposure therapy:
- Identify feared situations
- Gradually face these situations
- Learn coping strategies
For instance, if social situations cause anxiety, exposure therapy involves gradual exposure. Start with less intimidating scenarios. Over time, face more challenging situations. This process can reduce fear and build confidence.
Exposure therapy supports individuals in overcoming avoidance behaviors. It encourages facing and managing fears constructively.
CBT vs. Other Therapies
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a popular treatment for depression. It focuses on changing negative thought patterns to improve mood. But how does it compare to other therapies? Let’s explore how CBT measures up against medications, psychodynamic therapy, and mindfulness approaches.
Medication Comparison
CBT and medication are both common treatments for depression. Each has its strengths and weaknesses. Here’s how they compare:
- Effectiveness: Both can reduce symptoms of depression. Some studies show CBT is as effective as antidepressants for mild to moderate depression.
- Side Effects: Medications often have side effects like weight gain and fatigue. CBT has no physical side effects.
- Duration: Medications work quickly, sometimes in weeks. CBT may take longer to show results but can provide lasting skills.
| Factor | CBT | Medication |
| Side Effects | None | Possible |
| Time to Effect | Varies | Weeks |
| Long-term Benefits | Yes | Limited |
CBT empowers individuals by teaching coping skills. Medications might be a quicker fix but don’t offer the same personal growth.
Psychodynamic Therapy
Psychodynamic therapy and CBT differ in their approach to depression.
- Focus: Psychodynamic therapy explores the unconscious mind and past experiences. CBT focuses on current thoughts and behaviors.
- Duration: Psychodynamic therapy is often long-term. CBT tends to be shorter, typically 12 to 20 sessions.
- Goal: Psychodynamic therapy aims to uncover deep-rooted issues. CBT aims to change specific thought patterns.
Psychodynamic therapy can be insightful. It helps understand the root causes of depression. But this insight may take time. CBT offers practical tools for immediate use. This makes it more action-oriented.
Both therapies have their place. Some find value in understanding their past. Others prefer actionable steps to improve daily life.
Mindfulness Approaches
Mindfulness approaches are gaining popularity. They offer another way to treat depression. How do they compare to CBT?
- Technique: Mindfulness teaches awareness and acceptance of thoughts. CBT focuses on changing negative thoughts.
- Practice: Mindfulness is often practiced through meditation. CBT involves structured sessions with a therapist.
- Outcome: Mindfulness can reduce stress and improve emotional regulation. CBT aims to change thought patterns and behaviors.
Mindfulness can complement CBT. It enhances self-awareness and reduces stress. CBT provides strategies to tackle negative thoughts.
Both can be used together for a comprehensive approach. Each has unique benefits. Combining them might offer the best results for some.
Benefits Of CBT for Depression
Depression affects many people around the world. It can make daily life hard. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) offers hope. CBT is a type of talk therapy. It helps people change their thinking patterns. This can improve how they feel. Let’s explore the benefits of CBT for depression.
Improves Negative Thought Patterns
CBT helps identify and change negative thoughts. These thoughts can worsen depression. By recognizing them, people can learn to think differently. This change can improve their mood. It helps them feel more in control.
Develops Coping Skills
CBT teaches useful coping skills. These skills help manage stress and anxiety. People learn how to handle difficult situations better. They also learn ways to prevent future depression episodes.
Promotes Behavioral Change
CBT encourages positive behavior changes. It helps people set goals and achieve them. This can boost their self-esteem and motivation. Small changes in behavior can lead to big improvements in mental health.
Provides Long-term Benefits
CBT offers long-lasting results. Unlike medication, its benefits continue even after therapy ends. People can use the skills learned in CBT throughout their lives. This makes it a valuable tool for managing depression.
Enhances Problem-solving Skills
CBT improves problem-solving abilities. People learn to tackle issues step-by-step. This approach reduces feelings of being overwhelmed. It helps people make better decisions and face challenges with confidence.
Reduces Risk Of Relapse
CBT lowers the chance of depression returning. The skills learned help people maintain their mental health. They become more resilient to stress and setbacks. This reduces the risk of future depression episodes.
| Benefit | Description |
| Improves Thought Patterns | Identifies and changes negative thinking. |
| Develops Coping Skills | Teaches methods to manage stress. |
| Promotes Behavioral Change | Encourages setting and achieving goals. |
| Provides Long-Term Benefits | Offers lasting results after therapy ends. |
| Enhances Problem-Solving Skills | Improves ability to tackle issues. |
| Reduces Risk of Relapse | Lowers chances of depression returning. |
Challenges In CBT
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a common method for treating depression. It involves identifying and changing negative thought patterns. While effective, CBT also comes with challenges. Understanding these challenges can help you better prepare for the therapy process.
Difficulty In Identifying Negative Thoughts
One major challenge is identifying negative thoughts. Many people are not aware of their own thought patterns. Often, these thoughts occur automatically and are deeply ingrained. This makes it hard to pinpoint and address them.
To overcome this, therapists may use tools like journaling. Writing down thoughts can reveal patterns and triggers. This is a crucial step for effective therapy.
Emotional Discomfort
CBT can bring emotional discomfort. Confronting negative thoughts and feelings is not easy. You may feel anxious or upset during sessions. This emotional discomfort can be a barrier to progress.
- Therapists help manage this discomfort.
- Relaxation techniques are often taught.
- Support from friends or family can be beneficial.
Time Commitment
CBT requires a significant time commitment. Consistent sessions are necessary to see progress. Each session builds on the last. This means regular attendance is crucial.
Many people find it difficult to fit therapy into their busy schedules. It’s important to prioritize and manage time effectively for the best results.
Expectation Vs. Reality
Some people expect quick results from CBT. This can lead to disappointment. Therapy is a gradual process and requires patience. Progress may be slow, but it is steady.
Setting realistic goals is essential. Discuss expectations with your therapist. This can help align your understanding of what CBT can achieve.
Resistance To Change
Resistance to change is another challenge. Some people find it hard to alter long-standing habits. Change requires effort and can be uncomfortable.
Therapists provide support and encouragement. They help clients focus on the benefits of change. This can increase motivation and reduce resistance.
Finding A Cbt Therapist
Finding the right therapist for Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for depression can be a crucial step towards better mental health. CBT is a structured method that focuses on changing negative thought patterns. A skilled therapist can guide you through this process, offering support and techniques to manage depression effectively. Choosing a therapist involves understanding what to look for and where to begin your search.
Qualifications To Look For
It’s important to find a therapist who is well-qualified. Look for professionals with a background in psychology or psychiatry. They should have specific training in CBT. Many therapists will list their qualifications on their websites or profiles.
- Licensed Psychologist
- Certified CBT Practitioner
- Experience in treating depression
Where To Search
Many resources are available for finding a CBT therapist. Online directories are a popular choice. They offer detailed information about therapists in your area.
- Online Directories: Websites like Psychology Today and Therapy Finder provide comprehensive lists.
- Local Clinics: Community health centers often have therapists on staff.
- Referrals: Ask your primary care doctor for recommendations.
Questions To Ask
Before committing to a therapist, it’s wise to ask questions. This helps ensure they are the right fit for your needs.
- What is your experience with CBT and depression?
- How do you structure your sessions?
- Do you offer virtual appointments?
Evaluating Compatibility
Comfort and trust are vital in a therapeutic relationship. Pay attention to how you feel during initial interactions. Effective therapy requires a good rapport between you and your therapist.
| Aspect | Consideration |
| Communication Style | Do they listen and respond well? |
| Empathy | Do you feel understood? |
| Professionalism | Are they punctual and respectful? |
CBT in Group Settings
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a common treatment for depression. It helps people change negative thought patterns. While many experience CBT in one-on-one sessions, group settings offer unique benefits. These settings provide a supportive environment where individuals can share experiences and learn from each other. Group CBT encourages interaction, making the therapy process more dynamic and engaging.
How Group CBT Works
Group CBT involves a small number of participants. Sessions are usually led by a trained therapist. Meetings occur weekly. Each session focuses on specific topics related to depression. These topics may include identifying negative thoughts, developing coping skills, and setting realistic goals.
Benefits Of Group CBT
- Shared Experiences: Participants realize they are not alone. This shared understanding reduces feelings of isolation.
- Peer Support: Group members offer support and encouragement. This helps in building self-esteem and confidence.
- Diverse Perspectives: Members provide different viewpoints. This diversity helps in discovering new coping strategies.
Structure Of A Typical Session
| Session Part | Description |
| Introduction | The therapist outlines the session’s goals. |
| Discussion | Members share experiences related to the topic. |
| Skill Building | The therapist introduces new CBT techniques. |
| Feedback | Participants discuss what they learned. |
Common Techniques Used
Several techniques are used in group CBT. Some popular methods include:
- Cognitive Restructuring: Identifying and challenging negative thoughts.
- Behavioral Activation: Encouraging activities that bring joy.
- Mindfulness: Promoting awareness of the present moment.
Who Can Benefit From Group CBT?
Group CBT is suitable for many individuals. It is ideal for those who find comfort in sharing experiences. People who appreciate diverse perspectives and peer support often benefit most. It is also helpful for those who enjoy interactive learning environments. Group CBT provides a cost-effective option compared to individual sessions.
Long-term Outcomes Of Cbt
Understanding depression requires more than just acknowledging its symptoms. It demands exploring effective treatments like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). CBT is a structured, time-limited approach that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns. But what about its long-term outcomes? Does CBT offer lasting relief for those battling depression? The answer is promising.
Long-term Stability
CBT provides tools that individuals can use long after therapy ends. These tools equip them to handle future challenges. Studies show that those who complete CBT often maintain improvements over time. They report fewer depressive episodes. Their life satisfaction remains high.
Improved Coping Mechanisms
- Enhanced problem-solving skills
- Better emotional regulation
- Increased resilience
CBT helps individuals develop robust coping mechanisms. They learn to face stressors with confidence. The skills gained during therapy continue to benefit them. Many find they can navigate life’s ups and downs more effectively.
Reduction In Relapse Rates
Relapse prevention is a key benefit of CBT. Research highlights a significant drop in relapse rates among those who undergo CBT. The therapy focuses on recognizing early warning signs. It empowers individuals to act swiftly, preventing full-blown depressive episodes.
Long-term Satisfaction
Clients often report a higher sense of well-being post-CBT. They feel more in control. Their relationships improve. Work performance often enhances. These changes contribute to a lasting sense of fulfillment. The positive impact of CBT extends beyond mental health. It enhances overall life quality.
Supporting Evidence
| Study | Outcome |
| Smith et al. (2020) | 75% maintained improvements after 1 year |
| Johnson et al. (2018) | 60% reported reduced relapse rates |
These studies underscore the efficacy of CBT. They highlight its potential to provide lasting benefits. For many, CBT is not just a temporary solution. It is a pathway to enduring mental health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Help With Depression?
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) helps by identifying negative thought patterns. It teaches coping skills to manage and reduce depressive symptoms. CBT empowers individuals to replace harmful thoughts with positive, constructive ones. This therapy promotes healthier emotional responses and encourages positive behavior changes, effectively alleviating depression.
What Are The 5 Steps Of CBT?
The 5 steps of CBT are: identify troubling situations, become aware of thoughts, recognize negative thinking, challenge negative thoughts, and replace them with positive thoughts. These steps help individuals manage and change thought patterns, improving mental health and emotional well-being effectively.
What Is The Cognitive Approach To Treating Depression?
The cognitive approach to treating depression focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns. Therapists help patients challenge and modify distorted beliefs. Techniques include cognitive restructuring, mindfulness, and behavioral activation. These methods aim to improve mood and reduce symptoms by promoting healthier thinking and coping strategies.
Conclusion
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy offers hope for those with depression. It teaches useful skills. These skills help manage negative thoughts. They also improve daily life. With practice, these strategies can lead to positive change. People often feel better and more in control.
Seeking help is a strong step forward. Support is available. Remember, you are not alone. Professional therapists can guide the journey. CBT might be the right choice for many. It’s worth exploring. Begin the path to a brighter future today.
Your mental health matters. Always take care of it.